Vibration Machines Manufacturer, Bridge Feeder, Dosing Feeder, Sand Cooler and more
Two shafts with centrifugal weights are operated in opposite directions via a toothed gear, this action creates linear vibrations. The drive power is generally transmitted via a Cardan shaft with a standard, stationary motor.
|
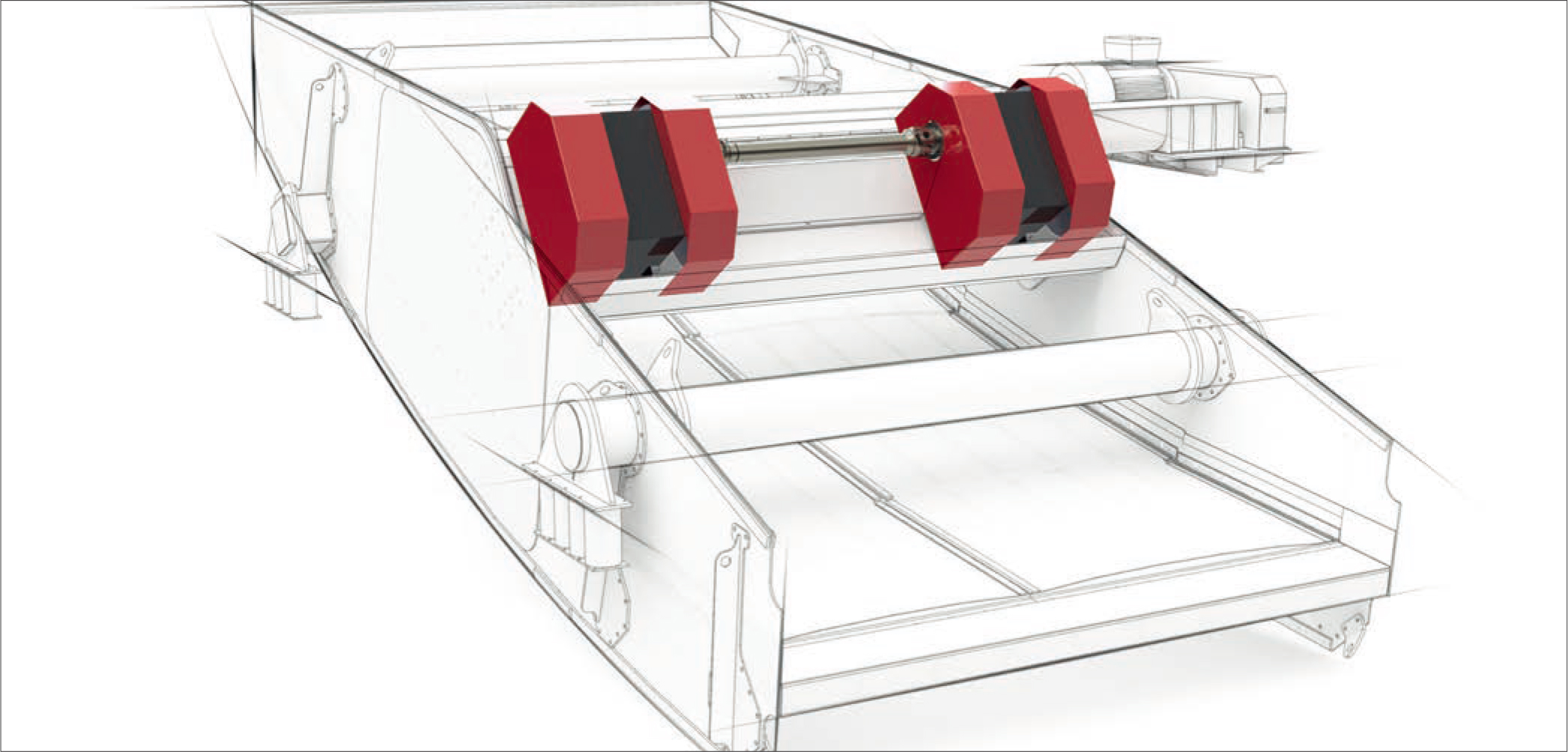
Heavy duty JVM® exciters are primarily used for large and heavy vibration machines. Their long service lives and problem-free operation even under the most difficult industrial conditions - testifies to the JVM® technical design all over the world. |
Machine conservation Forced mechanical synchronization dispenses with the critical synchronization phases and the associated high loadings during starting and stopping. The base machine construction is conservatively designed. |
|
Long services lives Instead of high-tension, welded designs, JR gearbox housings are manufactured exclusively from high-quality modular cast iron. The bearing arrangements consist of heavy-duty, high-quality bearings. The centrifugal weights are also protected by particularly sturdy hoods. |
Easy maintenance An oil splash system supplies the gears and bearings with a constant supply of lubrication. JVM® exciters can be operated in any position and are reliable in ambient temperatures of -40 ... +80°C (-40 ... +176°F) when the appropriate oil is used. |
Selection of Drive
construction weight when using one exciter.
*Approximate specification at medium deployment.
Dimension in mm
Variable parameters
With the machine off, the motion amplitude can be reliably set to the particular requirements by simply ad-justing the centrifugal weights. The motion frequency can also be adjusted via an optional frequency converter.
Drive
A standard hydraulic or 3-phase motor is used as the drive motor. Please note that the highest admissible speed of the exciter may not be exceeded and that the motor‘s starting torque must be 2.5-times that of the nominal tor queue.
Tip
Where extremely wide or heavy machines are necessary, several exciters can be operated in parallel side-by-side with one drive motor. The starting torque is thereby transmitted from one exciter to the next by coupling shafts.